
- Batch script example run filess how to#
- Batch script example run filess code#
- Batch script example run filess series#
- Batch script example run filess windows#
This is all about some methods and tricks to play with the “rename” or “ren” command. Will rename TESTA.txt to TESA, so it seems to mean chop off everything after the last S and then append an A. Will not change the name at all (remember: the last occurrence…?).

Pipe the output of Dir to Rename-Item and you’re in business. The two important commands you’ll need are Dir, which lists the files in the current directory, and Rename-Item, which renames an item (a file, in this case). Using PowerShell, you can pipe the output of one command-known as a “commandlet” in PowerShell terms-to another command, just like you can on Linux and other UNIX-like systems. PowerShell offers even more flexibility for renaming files in a command-line environment. The batch files can be used for many other simple actions like to delete files in bulk or to delete folders.

Batch script example run filess how to#
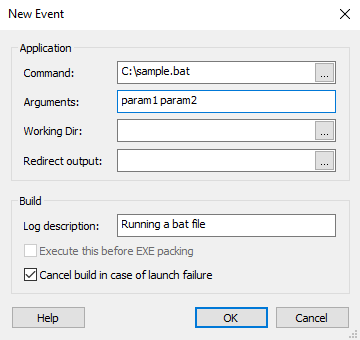
How to create a simple batch script to rename the file READ ALSO - Two different ways how to Change Directories in Command Prompt A batch file may contain any command the interpreter accepts interactively and use constructs that enable conditional branching and looping within the batch file, such as IF, FOR, and GOTO labels.
Batch script example run filess series#
Like using the rename command, you can also use the move command to rename a file as shown. A batch file is a script file in DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows.It consists of a series of commands to be executed by the command-line interpreter, stored in a plain text file. Rename a single file with the move command The command will create a copy of the original files with the new extension.
Batch script example run filess windows#
Use the following command at the Windows command line or within a batch file. Since the “rename” command can address extensions, you can also use it to change the extensions of the file. For example, if the file was in the “C:” directory, you would type a command similar to the following example. If the “TESTA.txt” file is not located in your current directory, you must specify the path to the file as a prefix to the file name. You need to be located at the CMD on the folder where the file is. The above command will rename the file name “TESTA.txt” to “TESTB.txt”.
Batch script example run filess code#
Note! The quotation marks in the command are only required if the name includes spaces. Windows Shell / Useful Batch File Examples This page provides examples of useful batch files and nuggets of code that can be used in batch files.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
